Why Does Legacy System Integration Matter for Insurance and Voice AI?

Amir Prodensky
CEO
Dec 8, 2025
11 min read
Modern voice AI for insurance without breaking legacy systems
Legacy systems in insurance are outdated software and hardware, often built with old languages like COBOL and running on mainframes like IBM z/OS.
These systems are complex, costly to maintain, and lack modern APIs. Plus, many skilled programmers are retiring, leaving knowledge gaps and silos.
Integrating these legacy systems with voice AI through legacy system integration is the smart way to modernize without risky full replacements. It speeds up results and minimizes disruption compared to large-scale legacy system replacement.
You’ll see benefits like:
Automated claims processing and policy management.
Voice self-service and personalized customer experiences.
Lower IT costs and reduced manual work.
Easier compliance with regulations through controlled API gateways.
Yet, before talking about integration, it helps to understand what legacy systems actually are.
What are legacy systems, and why do insurance companies still use them?
Legacy systems are older software and hardware that insurance companies rely on daily. Think of core mainframe systems running COBOL batch jobs handling claims adjudication or policy administration.
Others include Oracle E-Business Suite for finance, Peoplesoft HR modules, and IBM VSAM data stores for transaction processing. These systems have been around for decades, yet they still power many insurance operations.
You might wonder why companies stick with these old setups. The answer boils down to stability and cost, especially when weighed against a legacy system replacement strategy.
Legacy systems handle heavy transaction loads reliably.
Replacing them isn’t easy. It often means budgets stretching over multiple years, complex testing, and huge business risks, which is why legacy system integration is usually the safer option.
Plus, many niche insurance functions have no modern alternative tested enough to trust, which makes legacy system replacement difficult to justify.
That said, holding on to legacy systems comes with risks and limits:
Outdated security protocols, like weak encryption and patching gaps.
Mainframes that don’t scale well horizontally.
Data silos stopping a unified customer view.
Few or obsolete APIs that block integration and digital innovation, slowing down legacy system modernisation.
Legacy environments typically run on IBM z/OS mainframes using COBOL or PL/I languages and CICS for transaction processing. The COBOL programming community is shrinking, making it harder to maintain these systems.
Tools like Micro Focus Enterprise Analyzer or Heirloom Computing help analyze legacy code for better documentation and risk checks. Still, technical debt piles up, and onboarding new developers gets tougher over time, slowing down insurance legacy system transformation.
That’s where Strada helps. It works alongside legacy systems by offering AI-powered phone agents that connect securely via APIs or middleware. You keep your trusted backends but gain smart voice interactions and workflows.
This approach extends your legacy systems without needing full transformation – perfect for insurance legacy system transformation and legacy system extension projects.
Legacy systems may be old, but they still run the core of insurance operations. That’s exactly why integrating them with voice AI delivers so much value without forcing risky replacements.
What are the benefits of integrating legacy systems with voice AI in insurance?
You’re probably wondering why integrating voice AI with legacy systems makes more sense than committing to a full legacy system replacement strategy. Simply put, it can cut project costs and timelines by 30-60%, according to Gartner and Forrester reports.
To understand why integration wins so often, it helps to compare it directly with full system replacement.

That’s a huge saving for insurers who want to upgrade without massive disruptions during insurance legacy system transformation.
Cost and operational efficiency gains
Beyond cost, integration drives real operational wins. Voice bots can automate busy workflows like claims intake and policy updates by directly interacting with your legacy systems.
This cuts manual data entry errors and trims down repeat calls to your service center.
Plus, customers get answers faster with virtual assist pulling data from both old and new sources to offer rich, context-aware conversations.
They can check policies or billing info hands-free using Alexa Skills or Google Assistant Actions, which seriously reduces hold times.
Access to modern AI and voice technologies
Integrating voice AI with legacy systems lets insurers add modern language and speech capabilities without rebuilding their core platforms, which is the essence of legacy system extension.
You keep the backbone, but upgrade what the caller actually experiences.
In practice, this looks like:
Intent understanding and dialog control with IBM Watson Assistant or Google Dialogflow, plus voice command handling via Amazon Lex.
Multilingual speech-to-text and text-to-speech with Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services across voice and digital channels.
Secure legacy data access through AWS API Gateway or Apigee Edge using OAuth 2.0 and JWT, with centralized logging for audit trails.
Faster launches of voice-driven services like quotes, micro-insurance, and real-time claim updates using OpenLegacy, Nividous RPA, MuleSoft Anypoint, Dell Boomi, AWS Lambda, or Azure Functions.
These tools don’t replace your core systems. They wrap them with a modern voice layer that’s easier to scale, secure, and improve over time.
Insurance-ready voice AI in practice
One standout solution is Strada.
It delivers instant AI-powered phone agents designed specifically for insurance tasks like renewals, First Notice of Loss claims, policy servicing, and quote intake. Strada handles repetitive calls and smartly routes complex issues to humans.
This cuts costs, boosts efficiency, and elevates customer satisfaction. Best of all, Strada’s AI is trained on insurance lingo, ensuring its voice understanding is spot-on. It integrates smoothly via APIs or your current AMS/CRM – no expensive redevelopment needed.
Before you move forward, it’s important to understand the challenges teams usually face.
What challenges come with integrating legacy insurance systems for voice AI?
Integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems isn’t always smooth sailing. You’ll face several hurdles, but knowing them upfront helps you tackle each one effectively.
Security and integration complexity
Integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems often surfaces issues that were hidden for years. Most of them aren’t blockers, but they do add friction if you don’t plan for them early.
In practice, teams usually run into the following challenges:
Legacy systems lacking encryption and relying on outdated protocols like SNA or CIFS.
Missing or outdated APIs that require reverse-engineering batch logic or data access layers.
Strict compliance requirements across claims, underwriting, and policy workflows under HIPAA or GDPR.
High technical debt combined with limited internal expertise and incomplete documentation.
Addressing them upfront with proper security layers, clear integration boundaries, and realistic expectations makes voice AI rollouts far more predictable.
Operational constraints and scalability limits
Testing is another challenge. Voice AI needs clean, timely data, but legacy systems often work in batches, not in real time. Balancing this mismatch means setting up detailed integration tests using voice simulation tools like Postman or Botium.
And don’t forget scalability. Legacy infrastructure wasn’t designed for low-latency, real-time interactions. Adding caching layers or event-driven messaging with Apache Kafka or IBM MQ can help meet voice AI’s speed demands.
Supporting employees through AI adoption
Finally, your workforce will need support. They’ll juggle new voice AI tools alongside old processes. Retraining and managing change smoothly, with frameworks like ADKAR or Kotter, makes adoption easier.
You might be wondering how to overcome these challenges seamlessly. Strada offers no-engineering-lift AI agents that plug right into your existing telephony and insurance systems.
Its workflow automation cuts down manual handoffs, speeds ROI, and keeps security and compliance on point.
Plus, Strada’s forward-deployed team guides you through security, performance, and integration best practices, easing your legacy exposure worries and boosting your voice AI success.
The good news is that these challenges are well understood. There are proven integration approaches that work reliably in insurance.
How can you integrate legacy systems with voice AI? Practical approaches and tools
Integrating legacy systems with voice AI might sound tricky, but with the right approaches, you can make it work smoothly. You’ll learn practical ways to connect your older insurance systems with new voice AI tech without massive overhauls.
Let’s break down the key methods and tools that enable legacy system extension in practice.
Core integration patterns for legacy systems
There are a few proven ways teams connect voice AI to legacy systems. Seeing them visually makes the trade-offs clearer.

First up, API strategies are your best friend. By exposing or wrapping legacy features into RESTful, SOAP, or GraphQL APIs, you create a clear bridge for voice AI to interact with your systems.
Use API design tools like Swagger/OpenAPI or RAML to document these interfaces, so everyone understands how they work.
During development, Postman helps you test and tweak APIs easily. This approach enables you to extend legacy systems without rewriting them.
If APIs feel insufficient or too complex, middleware and Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) platforms come to the rescue. Tools like MuleSoft Anypoint, WSO2, or IBM Integration Bus orchestrate communication between your voice AI platform and both legacy and modern systems.
They handle protocol translation and message enrichment, which means your voice AI speaks the right language behind the scenes.
Another handy option is Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) – cloud tools like Dell Boomi, Microsoft Power Automate, and Zapier simplify connecting different systems quickly.
They offer drag-and-drop interfaces, which get your integrations off the ground fast and with minimal coding. If you want to automate routine workflows without deep technical involvement, this is ideal.
Sometimes, your legacy system might not have APIs or be too complex to open up directly. That’s where Robotic Process Automation (RPA) steps in. Bots built with platforms like Nividous RPA or UIPath can mimic human interactions with legacy screen interfaces.
This way, you automate data entry or retrieval tasks while keeping your existing systems intact.
At this point, it helps to pause and look at these integration options side by side. Each one solves a different problem, and seeing them together makes the trade-offs easier to understand.
Integration approach | What it’s best for | When teams use it | Main trade-off |
APIs (REST, SOAP, GraphQL) | Direct system access | You control the backend | Requires dev effort |
Middleware / ESB | Connecting many systems | Large, complex stacks | Higher setup complexity |
iPaaS | Fast cloud integrations | Speed matters most | Less customization |
RPA | No APIs available | UI-only legacy systems | Fragile at scale |
As systems evolve, integration often becomes a mix of methods – bridging on-premise legacy platforms with cloud services while modernizing components step by step.
Many organizations find combining cloud and on-premises tech beneficial. Using solutions such as OpenLegacy Hub, you can create a hybrid integration environment.
This setup allows secure and scalable API exposure from legacy systems connected smoothly to cloud-based voice AI services.
If you plan to evolve your tech stack more gradually, consider breaking down your old monolith systems into microservices using frameworks like Spring Boot or Quarkus.
Smaller, modular components make it easier to attach voice AI features incrementally, while improving scalability.
Scalability, reliability, and operational readiness
To make communication more resilient and scalable, introduce event-driven messaging. Platforms like Apache Kafka, IBM MQ, or RabbitMQ support asynchronous message queues.
This reduces synchronization bottlenecks and helps your voice AI handle real-time data flows without overloading legacy systems.
When modernizing hosting environments, containerization with Docker and Kubernetes lets you run legacy apps in portable, cloud-friendly setups. This approach also paves the way for DevOps practices like continuous deployment, speeding up feature rollout.
Of course, you’ll want to keep everything secure. Implement industry-standard security frameworks such as OAuth 2.0, JWT, multi-factor authentication, and TLS encryption for data at rest and in transit. API gateways like Apigee, AWS API Gateway, or IBM API.
Connect centrally manage security policies, making your integrations safer and compliant with insurance regulations.
To keep your integrations stable and efficient, focus on API management and monitoring. Use tools like Kong or Tyk for API gateway functions.
Meanwhile, monitoring stacks like ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Prometheus, and Grafana give you clear visibility and help catch issues before they snowball.
If you want to speed up integration projects and empower non-developers, low-code/no-code frameworks such as Microsoft PowerApps, Mendix, and OutSystems enable rapid voice AI deployments.
These platforms open the door for citizen developers to build and adjust integrations without waiting for IT cycles.
For building your voice AI layer, go with popular platforms like Google Dialogflow or Amazon Lex for voice interfaces and intent recognition. IBM Watson Assistant offers sophisticated dialog management, while Microsoft Azure Bot Service supports multi-modal interactions, combining voice, text, and more.
One last game changer: establish robust CI/CD pipelines. Tools like Azure DevOps, Jenkins, or GitLab CI let you integrate API development and voice AI deployment seamlessly.
By this point, it helps to see how all production pieces come together as one system.
Component | What it enables | Why it matters |
Event-driven messaging | Async processing | Handles traffic spikes |
Containers | Portable runtimes | Safer scaling |
Security frameworks | Controlled access | Protects sensitive data |
API management | Traffic control | Prevents overload |
Monitoring | System visibility | Faster incident response |
CI/CD pipelines | Automated releases | Continuous improvement |
Continuous integration ensures you can roll out improvements quickly and reliably, keeping your systems in sync.
A faster path with insurance-ready voice AI
To make things even simpler, consider Strada’s plug-and-play AI phone agents. These agents integrate natively with legacy AMS, CRM, and telephony platforms, cutting down engineering effort drastically and speeding up deployment.
Plus, Strada Workflows empower you with drag-and-drop, no-code automation for post-call actions, like triggering follow-ups, updating your CRM, or starting multi-channel communications – connecting your voice AI directly to business processes without writing custom code.

In summary, integrating legacy systems with voice AI isn’t magic – it’s all about choosing the right combination of APIs, middleware, automation tools, and platforms.
By mixing and matching these practical solutions, you’ll extend your legacy systems’ value and make voice AI work seamlessly for your insurance business.
Once the approach is clear, execution becomes manageable. Breaking integration into clear steps reduces risk and keeps teams aligned.
How to plan and execute integration step-by-step
When you’re integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems, a solid plan is your best friend.
You’ll want to move carefully but confidently, especially when avoiding full legacy system replacement.
Here’s how to break it down:
Assess legacy system landscape
Start by taking stock of what you have. Make a detailed list of legacy applications, data stores, batch jobs, and middleware components.
Gather architecture documents, check existing APIs, and see how complete the documentation is using tools like Enterprise Architect or Sparx Systems.
Also, look at how often these systems are used and which ones are critical. This gives you the big picture and helps avoid surprises later.
Define voice AI use cases aligned to business priorities
Next, pick voice AI use cases that matter most to your business. Think automation for claims intake via voice bots, virtual assistants answering policy queries, or voice-driven billing updates.
Get input from stakeholders to make sure these ideas deliver real value and a solid return on investment.
Select integration technologies
Choose the right tools based on what your legacy systems can handle and what your voice AI requires. You might use middleware, API platforms, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), or a combination.
Vendors like OpenLegacy, Nividous, MuleSoft, or Dell Boomi are strong contenders. Look for solutions that scale well, keep data secure, and come with good support.
To keep things practical, here’s a quick checklist for this step:
Confirm legacy system’s API readiness.
Decide between middleware, RPA, or hybrid approach.
Evaluate vendor scalability and security features.
Ensure support and training availability.
Once these basics are clear, teams can move forward with confidence and avoid costly rework later.
Build prototypes and conduct integration testing
Create prototypes in sandbox or staging environments. Use API testing tools like Postman or SoapUI to validate connections. For your voice AI, employ testing suites such as Botium to check intent accuracy and user experience.
Load testing is key too, to avoid performance issues. Also, double-check compliance with data security and privacy rules here.
For example, while testing, you can incorporate pilot AI phone agents powered by Strada, which come with built-in insurance workflows like claim filing and policy servicing. This helps validate benefits early, with minimal impact on your live legacy systems.
Strada’s pre-built insurance use cases and domain models speed up your proof of concept and make deployment smoother.
Optimize integrations
Once testing is done, tune the system for speed and accuracy. Improve API response times and boost voice AI’s intent recognition. Don’t forget security hardening – set up strong authentication and encryption.
Also, put rollback plans and incident response procedures in place to keep things stable and easy to recover.
Document everything and train your teams
Hungry for smooth operations? Document every integration workflow clearly. Create runbooks, detailed API documentation, and user manuals. Then, run training sessions for IT and customer service teams.
Using knowledge bases and learning management systems will help keep everyone up to speed over time.
Plan for scalability and maintainability
Voice AI integration shouldn’t be treated as a one-off project. Planning for growth early helps avoid brittle setups that break as usage, traffic, or requirements change.
In practice, this means:
Designing integrations so components can scale independently as call volumes grow.
Using containerization and cloud-ready patterns to simplify deployment and rollback.
Putting version control and change management in place to prevent breaking updates.
Accounting for future voice AI features to avoid reworking integrations later.
This approach keeps integrations stable over time and allows teams to evolve voice AI capabilities without constantly revisiting core system architecture.
Set up monitoring and continuous improvement
Finally, build monitoring dashboards using tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or the ELK stack. These help you track voice AI and API health in real time. Set alerts for any SLA breaches or odd behavior.
Establish feedback loops with business users and tech teams to keep refining performance continuously.
Supporting your integration work, integrate DevOps tools like Azure DevOps or AWS CodePipeline to automate builds and deployments. The Nividous Control Center is another great tool to keep RPA bots healthy and governed properly.
By following these steps, you turn the daunting task of legacy system modernisation and voice AI integration into a manageable, successful journey. You’ll not only make your systems smarter but also prepare your insurance operations for the future.
So what does all this effort enable in practice? Let’s look at how insurers actually use voice AI today!
What are common voice AI use cases integrated with legacy systems in insurance?
You’re probably wondering how voice AI can actually work with those old legacy systems insurers use. The good news? Voice AI integration is already transforming core insurance operations, making life easier for customers, agents, and insurers alike.
Let’s walk through a simple, real-world example to see how this works in practice.
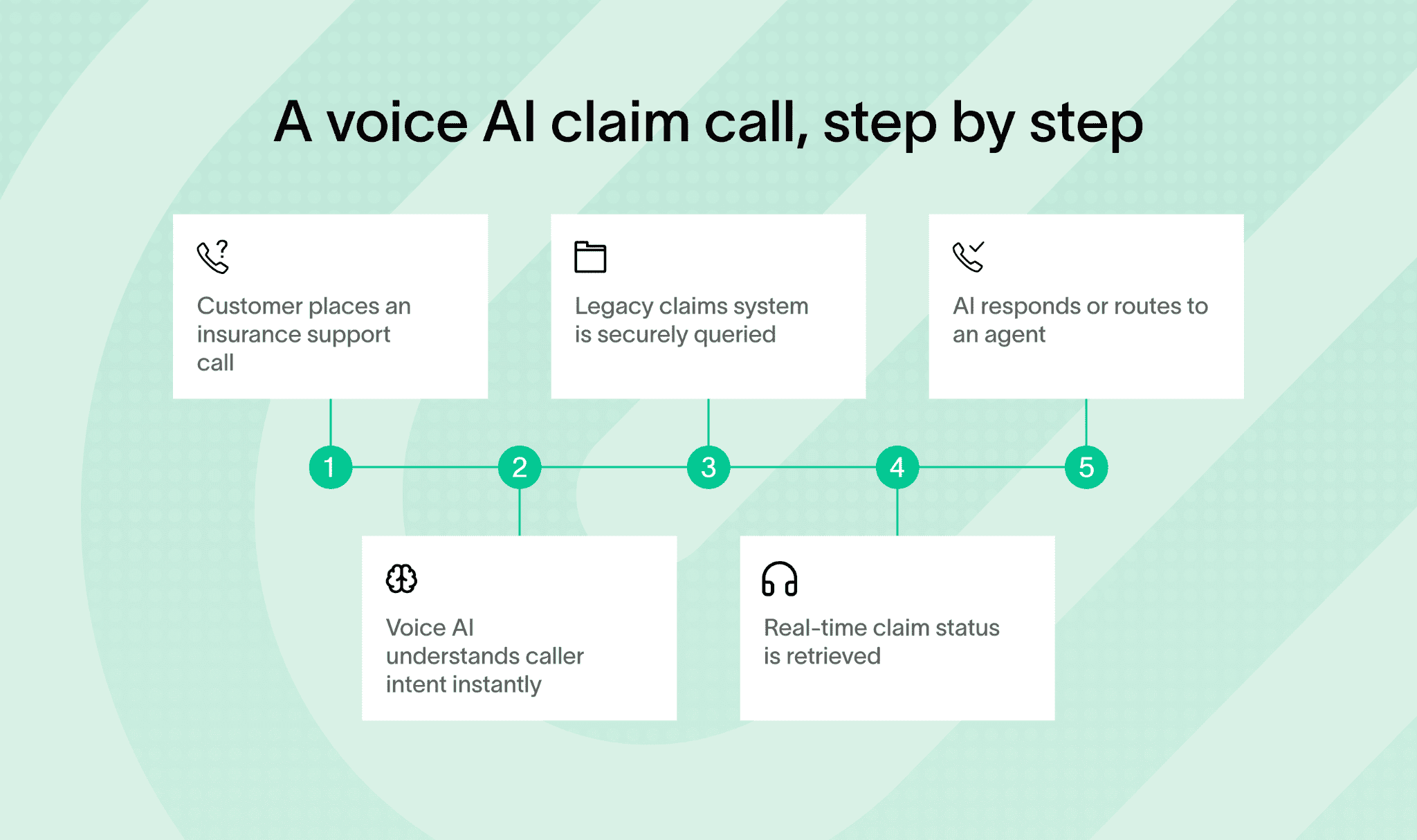
And, let’s walk through some of the most practical and common use cases where voice AI teams up with legacy systems.
Core insurance operations powered by voice AI
First off, customer service is a big one. Conversational AI can answer policy questions, explain coverage details, give claim status updates, and handle FAQs. This reduces the load on call centers by letting voice assistants tap directly into those backend legacy databases for real-time info.
That means customers get instant answers without waiting on hold, and agents can focus on more complex tasks.
Another popular use is claims filing and status tracking. You can use voice commands to start a new claim, leave voice notes about incidents, or check the progress of existing claims.
The AI talks to the legacy claims processing systems behind the scenes, making this process faster and less manual.
Extended and emerging insurance use cases
Here’s a quick list to show you how voice AI helps with other key insurance tasks by integrating with legacy systems:
Underwriting assistance → Capture data from customers or agents by voice, then quickly query and update legacy underwriting engines through APIs to adjust policies on the fly.
Fraud detection → Voice-guided workflows offer real-time risk alerts, helping investigators adjust their approach using AI models connected to older risk databases.
Automated payment reconciliation → Confirm payments or trigger reconciliation checks via simple voice commands, with secure links to legacy financial platforms like Oracle EBS.
Micro-insurance access → In emerging markets, mobile voice platforms enable instant policy purchases or inquiries, all backed by middleware that bridges with legacy policy admin systems.
You’ll find several top voice AI platforms supporting these integrations. Google Dialogflow shines for intent mapping and multi-channel voice experiences, while IBM Watson Assistant lets you build customizable virtual agents that feel natural on calls.
Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services nails the speech-to-text and text-to-speech tasks, and Amazon Lex powers Alexa-enabled skills tailored for insurance workflows.
Voice AI use cases in production
In practical terms, Strada is a great example of making this work on the ground. Their AI phone agents handle thousands of calls, from quote intake and First Notice of Loss (FNOL) reporting to renewals and agent lead qualification.
These agents trigger workflows that dig deep into legacy systems, AMS, CRM, and others, automating complex tasks without replacing those legacy systems entirely.
Strada also automates certificate issuance requests and claims intake by interfacing directly with legacy policy and claims backends. This results in quick, personalized responses that boost customer satisfaction and make agents more productive.
You can see how this smart integration strikes the perfect balance – leveraging existing systems while adding exciting new voice AI capabilities.
By focusing on integrating voice AI with current legacy systems instead of replacing them wholesale, insurers gain efficiency and improve customer interactions rapidly.
You’ll learn that this approach not only cuts costs but also creates seamless, hands-free experiences customers expect.
At this point, the pattern is clear. Integration allows insurers to move forward without disrupting systems they already rely on.
Why integration beats replacement and how voice AI unlocks legacy value
You’ll find that integrating voice AI with your legacy systems makes more sense than pursuing a broad legacy system replacement strategy. It protects your big investments, avoids the high costs and risks of rewrites, and lets you innovate faster by layering AI over systems you already trust.
Voice AI boosts customer experience and operational agility by enabling real-time, natural conversations powered by your existing data.
To get started, try these practical steps:
Launch a pilot or proof-of-concept with platforms like OpenLegacy, Nividous, or MuleSoft to see real business impact quickly.
Engage expert partners early, align clearly with your business goals, and invest in ongoing training and monitoring for long-term success.
For insurance specifically, consider Strada. It’s a ready-to-use AI phone agent platform designed for deep legacy integration, zero engineering lift, and quick wins in call automation and AI workflows.
This way, you get immediate boosts in operations and revenue without the headaches of full legacy system modernisation or replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can voice AI work with very old insurance systems?
Yes. Voice AI can connect through APIs, middleware, or RPA, allowing interaction with even COBOL-based mainframes without replacing existing core insurance platforms.
How long does legacy system integration with voice AI usually take?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Do insurers need to replace their core systems to use voice AI?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Can voice AI scale during peak call volumes?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
How does voice AI reduce call center workload?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Table of Contents
Carriers, MGAs, and brokers scale revenue-driving phone calls with Strada's conversational AI platform.
Start scaling with voice AI agents today
Join innovative carriers and MGAs transforming their calls with Strada.
Why Does Legacy System Integration Matter for Insurance and Voice AI?

Amir Prodensky
CEO
Dec 8, 2025
11 min read
Modern voice AI for insurance without breaking legacy systems
Legacy systems in insurance are outdated software and hardware, often built with old languages like COBOL and running on mainframes like IBM z/OS.
These systems are complex, costly to maintain, and lack modern APIs. Plus, many skilled programmers are retiring, leaving knowledge gaps and silos.
Integrating these legacy systems with voice AI through legacy system integration is the smart way to modernize without risky full replacements. It speeds up results and minimizes disruption compared to large-scale legacy system replacement.
You’ll see benefits like:
Automated claims processing and policy management.
Voice self-service and personalized customer experiences.
Lower IT costs and reduced manual work.
Easier compliance with regulations through controlled API gateways.
Yet, before talking about integration, it helps to understand what legacy systems actually are.
What are legacy systems, and why do insurance companies still use them?
Legacy systems are older software and hardware that insurance companies rely on daily. Think of core mainframe systems running COBOL batch jobs handling claims adjudication or policy administration.
Others include Oracle E-Business Suite for finance, Peoplesoft HR modules, and IBM VSAM data stores for transaction processing. These systems have been around for decades, yet they still power many insurance operations.
You might wonder why companies stick with these old setups. The answer boils down to stability and cost, especially when weighed against a legacy system replacement strategy.
Legacy systems handle heavy transaction loads reliably.
Replacing them isn’t easy. It often means budgets stretching over multiple years, complex testing, and huge business risks, which is why legacy system integration is usually the safer option.
Plus, many niche insurance functions have no modern alternative tested enough to trust, which makes legacy system replacement difficult to justify.
That said, holding on to legacy systems comes with risks and limits:
Outdated security protocols, like weak encryption and patching gaps.
Mainframes that don’t scale well horizontally.
Data silos stopping a unified customer view.
Few or obsolete APIs that block integration and digital innovation, slowing down legacy system modernisation.
Legacy environments typically run on IBM z/OS mainframes using COBOL or PL/I languages and CICS for transaction processing. The COBOL programming community is shrinking, making it harder to maintain these systems.
Tools like Micro Focus Enterprise Analyzer or Heirloom Computing help analyze legacy code for better documentation and risk checks. Still, technical debt piles up, and onboarding new developers gets tougher over time, slowing down insurance legacy system transformation.
That’s where Strada helps. It works alongside legacy systems by offering AI-powered phone agents that connect securely via APIs or middleware. You keep your trusted backends but gain smart voice interactions and workflows.
This approach extends your legacy systems without needing full transformation – perfect for insurance legacy system transformation and legacy system extension projects.
Legacy systems may be old, but they still run the core of insurance operations. That’s exactly why integrating them with voice AI delivers so much value without forcing risky replacements.
What are the benefits of integrating legacy systems with voice AI in insurance?
You’re probably wondering why integrating voice AI with legacy systems makes more sense than committing to a full legacy system replacement strategy. Simply put, it can cut project costs and timelines by 30-60%, according to Gartner and Forrester reports.
To understand why integration wins so often, it helps to compare it directly with full system replacement.

That’s a huge saving for insurers who want to upgrade without massive disruptions during insurance legacy system transformation.
Cost and operational efficiency gains
Beyond cost, integration drives real operational wins. Voice bots can automate busy workflows like claims intake and policy updates by directly interacting with your legacy systems.
This cuts manual data entry errors and trims down repeat calls to your service center.
Plus, customers get answers faster with virtual assist pulling data from both old and new sources to offer rich, context-aware conversations.
They can check policies or billing info hands-free using Alexa Skills or Google Assistant Actions, which seriously reduces hold times.
Access to modern AI and voice technologies
Integrating voice AI with legacy systems lets insurers add modern language and speech capabilities without rebuilding their core platforms, which is the essence of legacy system extension.
You keep the backbone, but upgrade what the caller actually experiences.
In practice, this looks like:
Intent understanding and dialog control with IBM Watson Assistant or Google Dialogflow, plus voice command handling via Amazon Lex.
Multilingual speech-to-text and text-to-speech with Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services across voice and digital channels.
Secure legacy data access through AWS API Gateway or Apigee Edge using OAuth 2.0 and JWT, with centralized logging for audit trails.
Faster launches of voice-driven services like quotes, micro-insurance, and real-time claim updates using OpenLegacy, Nividous RPA, MuleSoft Anypoint, Dell Boomi, AWS Lambda, or Azure Functions.
These tools don’t replace your core systems. They wrap them with a modern voice layer that’s easier to scale, secure, and improve over time.
Insurance-ready voice AI in practice
One standout solution is Strada.
It delivers instant AI-powered phone agents designed specifically for insurance tasks like renewals, First Notice of Loss claims, policy servicing, and quote intake. Strada handles repetitive calls and smartly routes complex issues to humans.
This cuts costs, boosts efficiency, and elevates customer satisfaction. Best of all, Strada’s AI is trained on insurance lingo, ensuring its voice understanding is spot-on. It integrates smoothly via APIs or your current AMS/CRM – no expensive redevelopment needed.
Before you move forward, it’s important to understand the challenges teams usually face.
What challenges come with integrating legacy insurance systems for voice AI?
Integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems isn’t always smooth sailing. You’ll face several hurdles, but knowing them upfront helps you tackle each one effectively.
Security and integration complexity
Integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems often surfaces issues that were hidden for years. Most of them aren’t blockers, but they do add friction if you don’t plan for them early.
In practice, teams usually run into the following challenges:
Legacy systems lacking encryption and relying on outdated protocols like SNA or CIFS.
Missing or outdated APIs that require reverse-engineering batch logic or data access layers.
Strict compliance requirements across claims, underwriting, and policy workflows under HIPAA or GDPR.
High technical debt combined with limited internal expertise and incomplete documentation.
Addressing them upfront with proper security layers, clear integration boundaries, and realistic expectations makes voice AI rollouts far more predictable.
Operational constraints and scalability limits
Testing is another challenge. Voice AI needs clean, timely data, but legacy systems often work in batches, not in real time. Balancing this mismatch means setting up detailed integration tests using voice simulation tools like Postman or Botium.
And don’t forget scalability. Legacy infrastructure wasn’t designed for low-latency, real-time interactions. Adding caching layers or event-driven messaging with Apache Kafka or IBM MQ can help meet voice AI’s speed demands.
Supporting employees through AI adoption
Finally, your workforce will need support. They’ll juggle new voice AI tools alongside old processes. Retraining and managing change smoothly, with frameworks like ADKAR or Kotter, makes adoption easier.
You might be wondering how to overcome these challenges seamlessly. Strada offers no-engineering-lift AI agents that plug right into your existing telephony and insurance systems.
Its workflow automation cuts down manual handoffs, speeds ROI, and keeps security and compliance on point.
Plus, Strada’s forward-deployed team guides you through security, performance, and integration best practices, easing your legacy exposure worries and boosting your voice AI success.
The good news is that these challenges are well understood. There are proven integration approaches that work reliably in insurance.
How can you integrate legacy systems with voice AI? Practical approaches and tools
Integrating legacy systems with voice AI might sound tricky, but with the right approaches, you can make it work smoothly. You’ll learn practical ways to connect your older insurance systems with new voice AI tech without massive overhauls.
Let’s break down the key methods and tools that enable legacy system extension in practice.
Core integration patterns for legacy systems
There are a few proven ways teams connect voice AI to legacy systems. Seeing them visually makes the trade-offs clearer.

First up, API strategies are your best friend. By exposing or wrapping legacy features into RESTful, SOAP, or GraphQL APIs, you create a clear bridge for voice AI to interact with your systems.
Use API design tools like Swagger/OpenAPI or RAML to document these interfaces, so everyone understands how they work.
During development, Postman helps you test and tweak APIs easily. This approach enables you to extend legacy systems without rewriting them.
If APIs feel insufficient or too complex, middleware and Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) platforms come to the rescue. Tools like MuleSoft Anypoint, WSO2, or IBM Integration Bus orchestrate communication between your voice AI platform and both legacy and modern systems.
They handle protocol translation and message enrichment, which means your voice AI speaks the right language behind the scenes.
Another handy option is Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) – cloud tools like Dell Boomi, Microsoft Power Automate, and Zapier simplify connecting different systems quickly.
They offer drag-and-drop interfaces, which get your integrations off the ground fast and with minimal coding. If you want to automate routine workflows without deep technical involvement, this is ideal.
Sometimes, your legacy system might not have APIs or be too complex to open up directly. That’s where Robotic Process Automation (RPA) steps in. Bots built with platforms like Nividous RPA or UIPath can mimic human interactions with legacy screen interfaces.
This way, you automate data entry or retrieval tasks while keeping your existing systems intact.
At this point, it helps to pause and look at these integration options side by side. Each one solves a different problem, and seeing them together makes the trade-offs easier to understand.
Integration approach | What it’s best for | When teams use it | Main trade-off |
APIs (REST, SOAP, GraphQL) | Direct system access | You control the backend | Requires dev effort |
Middleware / ESB | Connecting many systems | Large, complex stacks | Higher setup complexity |
iPaaS | Fast cloud integrations | Speed matters most | Less customization |
RPA | No APIs available | UI-only legacy systems | Fragile at scale |
As systems evolve, integration often becomes a mix of methods – bridging on-premise legacy platforms with cloud services while modernizing components step by step.
Many organizations find combining cloud and on-premises tech beneficial. Using solutions such as OpenLegacy Hub, you can create a hybrid integration environment.
This setup allows secure and scalable API exposure from legacy systems connected smoothly to cloud-based voice AI services.
If you plan to evolve your tech stack more gradually, consider breaking down your old monolith systems into microservices using frameworks like Spring Boot or Quarkus.
Smaller, modular components make it easier to attach voice AI features incrementally, while improving scalability.
Scalability, reliability, and operational readiness
To make communication more resilient and scalable, introduce event-driven messaging. Platforms like Apache Kafka, IBM MQ, or RabbitMQ support asynchronous message queues.
This reduces synchronization bottlenecks and helps your voice AI handle real-time data flows without overloading legacy systems.
When modernizing hosting environments, containerization with Docker and Kubernetes lets you run legacy apps in portable, cloud-friendly setups. This approach also paves the way for DevOps practices like continuous deployment, speeding up feature rollout.
Of course, you’ll want to keep everything secure. Implement industry-standard security frameworks such as OAuth 2.0, JWT, multi-factor authentication, and TLS encryption for data at rest and in transit. API gateways like Apigee, AWS API Gateway, or IBM API.
Connect centrally manage security policies, making your integrations safer and compliant with insurance regulations.
To keep your integrations stable and efficient, focus on API management and monitoring. Use tools like Kong or Tyk for API gateway functions.
Meanwhile, monitoring stacks like ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Prometheus, and Grafana give you clear visibility and help catch issues before they snowball.
If you want to speed up integration projects and empower non-developers, low-code/no-code frameworks such as Microsoft PowerApps, Mendix, and OutSystems enable rapid voice AI deployments.
These platforms open the door for citizen developers to build and adjust integrations without waiting for IT cycles.
For building your voice AI layer, go with popular platforms like Google Dialogflow or Amazon Lex for voice interfaces and intent recognition. IBM Watson Assistant offers sophisticated dialog management, while Microsoft Azure Bot Service supports multi-modal interactions, combining voice, text, and more.
One last game changer: establish robust CI/CD pipelines. Tools like Azure DevOps, Jenkins, or GitLab CI let you integrate API development and voice AI deployment seamlessly.
By this point, it helps to see how all production pieces come together as one system.
Component | What it enables | Why it matters |
Event-driven messaging | Async processing | Handles traffic spikes |
Containers | Portable runtimes | Safer scaling |
Security frameworks | Controlled access | Protects sensitive data |
API management | Traffic control | Prevents overload |
Monitoring | System visibility | Faster incident response |
CI/CD pipelines | Automated releases | Continuous improvement |
Continuous integration ensures you can roll out improvements quickly and reliably, keeping your systems in sync.
A faster path with insurance-ready voice AI
To make things even simpler, consider Strada’s plug-and-play AI phone agents. These agents integrate natively with legacy AMS, CRM, and telephony platforms, cutting down engineering effort drastically and speeding up deployment.
Plus, Strada Workflows empower you with drag-and-drop, no-code automation for post-call actions, like triggering follow-ups, updating your CRM, or starting multi-channel communications – connecting your voice AI directly to business processes without writing custom code.

In summary, integrating legacy systems with voice AI isn’t magic – it’s all about choosing the right combination of APIs, middleware, automation tools, and platforms.
By mixing and matching these practical solutions, you’ll extend your legacy systems’ value and make voice AI work seamlessly for your insurance business.
Once the approach is clear, execution becomes manageable. Breaking integration into clear steps reduces risk and keeps teams aligned.
How to plan and execute integration step-by-step
When you’re integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems, a solid plan is your best friend.
You’ll want to move carefully but confidently, especially when avoiding full legacy system replacement.
Here’s how to break it down:
Assess legacy system landscape
Start by taking stock of what you have. Make a detailed list of legacy applications, data stores, batch jobs, and middleware components.
Gather architecture documents, check existing APIs, and see how complete the documentation is using tools like Enterprise Architect or Sparx Systems.
Also, look at how often these systems are used and which ones are critical. This gives you the big picture and helps avoid surprises later.
Define voice AI use cases aligned to business priorities
Next, pick voice AI use cases that matter most to your business. Think automation for claims intake via voice bots, virtual assistants answering policy queries, or voice-driven billing updates.
Get input from stakeholders to make sure these ideas deliver real value and a solid return on investment.
Select integration technologies
Choose the right tools based on what your legacy systems can handle and what your voice AI requires. You might use middleware, API platforms, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), or a combination.
Vendors like OpenLegacy, Nividous, MuleSoft, or Dell Boomi are strong contenders. Look for solutions that scale well, keep data secure, and come with good support.
To keep things practical, here’s a quick checklist for this step:
Confirm legacy system’s API readiness.
Decide between middleware, RPA, or hybrid approach.
Evaluate vendor scalability and security features.
Ensure support and training availability.
Once these basics are clear, teams can move forward with confidence and avoid costly rework later.
Build prototypes and conduct integration testing
Create prototypes in sandbox or staging environments. Use API testing tools like Postman or SoapUI to validate connections. For your voice AI, employ testing suites such as Botium to check intent accuracy and user experience.
Load testing is key too, to avoid performance issues. Also, double-check compliance with data security and privacy rules here.
For example, while testing, you can incorporate pilot AI phone agents powered by Strada, which come with built-in insurance workflows like claim filing and policy servicing. This helps validate benefits early, with minimal impact on your live legacy systems.
Strada’s pre-built insurance use cases and domain models speed up your proof of concept and make deployment smoother.
Optimize integrations
Once testing is done, tune the system for speed and accuracy. Improve API response times and boost voice AI’s intent recognition. Don’t forget security hardening – set up strong authentication and encryption.
Also, put rollback plans and incident response procedures in place to keep things stable and easy to recover.
Document everything and train your teams
Hungry for smooth operations? Document every integration workflow clearly. Create runbooks, detailed API documentation, and user manuals. Then, run training sessions for IT and customer service teams.
Using knowledge bases and learning management systems will help keep everyone up to speed over time.
Plan for scalability and maintainability
Voice AI integration shouldn’t be treated as a one-off project. Planning for growth early helps avoid brittle setups that break as usage, traffic, or requirements change.
In practice, this means:
Designing integrations so components can scale independently as call volumes grow.
Using containerization and cloud-ready patterns to simplify deployment and rollback.
Putting version control and change management in place to prevent breaking updates.
Accounting for future voice AI features to avoid reworking integrations later.
This approach keeps integrations stable over time and allows teams to evolve voice AI capabilities without constantly revisiting core system architecture.
Set up monitoring and continuous improvement
Finally, build monitoring dashboards using tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or the ELK stack. These help you track voice AI and API health in real time. Set alerts for any SLA breaches or odd behavior.
Establish feedback loops with business users and tech teams to keep refining performance continuously.
Supporting your integration work, integrate DevOps tools like Azure DevOps or AWS CodePipeline to automate builds and deployments. The Nividous Control Center is another great tool to keep RPA bots healthy and governed properly.
By following these steps, you turn the daunting task of legacy system modernisation and voice AI integration into a manageable, successful journey. You’ll not only make your systems smarter but also prepare your insurance operations for the future.
So what does all this effort enable in practice? Let’s look at how insurers actually use voice AI today!
What are common voice AI use cases integrated with legacy systems in insurance?
You’re probably wondering how voice AI can actually work with those old legacy systems insurers use. The good news? Voice AI integration is already transforming core insurance operations, making life easier for customers, agents, and insurers alike.
Let’s walk through a simple, real-world example to see how this works in practice.

And, let’s walk through some of the most practical and common use cases where voice AI teams up with legacy systems.
Core insurance operations powered by voice AI
First off, customer service is a big one. Conversational AI can answer policy questions, explain coverage details, give claim status updates, and handle FAQs. This reduces the load on call centers by letting voice assistants tap directly into those backend legacy databases for real-time info.
That means customers get instant answers without waiting on hold, and agents can focus on more complex tasks.
Another popular use is claims filing and status tracking. You can use voice commands to start a new claim, leave voice notes about incidents, or check the progress of existing claims.
The AI talks to the legacy claims processing systems behind the scenes, making this process faster and less manual.
Extended and emerging insurance use cases
Here’s a quick list to show you how voice AI helps with other key insurance tasks by integrating with legacy systems:
Underwriting assistance → Capture data from customers or agents by voice, then quickly query and update legacy underwriting engines through APIs to adjust policies on the fly.
Fraud detection → Voice-guided workflows offer real-time risk alerts, helping investigators adjust their approach using AI models connected to older risk databases.
Automated payment reconciliation → Confirm payments or trigger reconciliation checks via simple voice commands, with secure links to legacy financial platforms like Oracle EBS.
Micro-insurance access → In emerging markets, mobile voice platforms enable instant policy purchases or inquiries, all backed by middleware that bridges with legacy policy admin systems.
You’ll find several top voice AI platforms supporting these integrations. Google Dialogflow shines for intent mapping and multi-channel voice experiences, while IBM Watson Assistant lets you build customizable virtual agents that feel natural on calls.
Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services nails the speech-to-text and text-to-speech tasks, and Amazon Lex powers Alexa-enabled skills tailored for insurance workflows.
Voice AI use cases in production
In practical terms, Strada is a great example of making this work on the ground. Their AI phone agents handle thousands of calls, from quote intake and First Notice of Loss (FNOL) reporting to renewals and agent lead qualification.
These agents trigger workflows that dig deep into legacy systems, AMS, CRM, and others, automating complex tasks without replacing those legacy systems entirely.
Strada also automates certificate issuance requests and claims intake by interfacing directly with legacy policy and claims backends. This results in quick, personalized responses that boost customer satisfaction and make agents more productive.

You can see how this smart integration strikes the perfect balance – leveraging existing systems while adding exciting new voice AI capabilities.
By focusing on integrating voice AI with current legacy systems instead of replacing them wholesale, insurers gain efficiency and improve customer interactions rapidly.
You’ll learn that this approach not only cuts costs but also creates seamless, hands-free experiences customers expect.
At this point, the pattern is clear. Integration allows insurers to move forward without disrupting systems they already rely on.
Why integration beats replacement and how voice AI unlocks legacy value
You’ll find that integrating voice AI with your legacy systems makes more sense than pursuing a broad legacy system replacement strategy. It protects your big investments, avoids the high costs and risks of rewrites, and lets you innovate faster by layering AI over systems you already trust.
Voice AI boosts customer experience and operational agility by enabling real-time, natural conversations powered by your existing data.
To get started, try these practical steps:
Launch a pilot or proof-of-concept with platforms like OpenLegacy, Nividous, or MuleSoft to see real business impact quickly.
Engage expert partners early, align clearly with your business goals, and invest in ongoing training and monitoring for long-term success.
For insurance specifically, consider Strada. It’s a ready-to-use AI phone agent platform designed for deep legacy integration, zero engineering lift, and quick wins in call automation and AI workflows.
This way, you get immediate boosts in operations and revenue without the headaches of full legacy system modernisation or replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can voice AI work with very old insurance systems?
Yes. Voice AI can connect through APIs, middleware, or RPA, allowing interaction with even COBOL-based mainframes without replacing existing core insurance platforms.
How long does legacy system integration with voice AI usually take?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Do insurers need to replace their core systems to use voice AI?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Can voice AI scale during peak call volumes?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
How does voice AI reduce call center workload?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Table of Contents
Carriers, MGAs, and brokers scale revenue-driving phone calls with Strada's conversational AI platform.
Start scaling with voice AI agents today
Join innovative carriers and MGAs transforming their calls with Strada.
Why Does Legacy System Integration Matter for Insurance and Voice AI?

Amir Prodensky
CEO
Dec 8, 2025
11 min read
Modern voice AI for insurance without breaking legacy systems
Legacy systems in insurance are outdated software and hardware, often built with old languages like COBOL and running on mainframes like IBM z/OS.
These systems are complex, costly to maintain, and lack modern APIs. Plus, many skilled programmers are retiring, leaving knowledge gaps and silos.
Integrating these legacy systems with voice AI through legacy system integration is the smart way to modernize without risky full replacements. It speeds up results and minimizes disruption compared to large-scale legacy system replacement.
You’ll see benefits like:
Automated claims processing and policy management.
Voice self-service and personalized customer experiences.
Lower IT costs and reduced manual work.
Easier compliance with regulations through controlled API gateways.
Yet, before talking about integration, it helps to understand what legacy systems actually are.
What are legacy systems, and why do insurance companies still use them?
Legacy systems are older software and hardware that insurance companies rely on daily. Think of core mainframe systems running COBOL batch jobs handling claims adjudication or policy administration.
Others include Oracle E-Business Suite for finance, Peoplesoft HR modules, and IBM VSAM data stores for transaction processing. These systems have been around for decades, yet they still power many insurance operations.
You might wonder why companies stick with these old setups. The answer boils down to stability and cost, especially when weighed against a legacy system replacement strategy.
Legacy systems handle heavy transaction loads reliably.
Replacing them isn’t easy. It often means budgets stretching over multiple years, complex testing, and huge business risks, which is why legacy system integration is usually the safer option.
Plus, many niche insurance functions have no modern alternative tested enough to trust, which makes legacy system replacement difficult to justify.
That said, holding on to legacy systems comes with risks and limits:
Outdated security protocols, like weak encryption and patching gaps.
Mainframes that don’t scale well horizontally.
Data silos stopping a unified customer view.
Few or obsolete APIs that block integration and digital innovation, slowing down legacy system modernisation.
Legacy environments typically run on IBM z/OS mainframes using COBOL or PL/I languages and CICS for transaction processing. The COBOL programming community is shrinking, making it harder to maintain these systems.
Tools like Micro Focus Enterprise Analyzer or Heirloom Computing help analyze legacy code for better documentation and risk checks. Still, technical debt piles up, and onboarding new developers gets tougher over time, slowing down insurance legacy system transformation.
That’s where Strada helps. It works alongside legacy systems by offering AI-powered phone agents that connect securely via APIs or middleware. You keep your trusted backends but gain smart voice interactions and workflows.
This approach extends your legacy systems without needing full transformation – perfect for insurance legacy system transformation and legacy system extension projects.
Legacy systems may be old, but they still run the core of insurance operations. That’s exactly why integrating them with voice AI delivers so much value without forcing risky replacements.
What are the benefits of integrating legacy systems with voice AI in insurance?
You’re probably wondering why integrating voice AI with legacy systems makes more sense than committing to a full legacy system replacement strategy. Simply put, it can cut project costs and timelines by 30-60%, according to Gartner and Forrester reports.
To understand why integration wins so often, it helps to compare it directly with full system replacement.

That’s a huge saving for insurers who want to upgrade without massive disruptions during insurance legacy system transformation.
Cost and operational efficiency gains
Beyond cost, integration drives real operational wins. Voice bots can automate busy workflows like claims intake and policy updates by directly interacting with your legacy systems.
This cuts manual data entry errors and trims down repeat calls to your service center.
Plus, customers get answers faster with virtual assist pulling data from both old and new sources to offer rich, context-aware conversations.
They can check policies or billing info hands-free using Alexa Skills or Google Assistant Actions, which seriously reduces hold times.
Access to modern AI and voice technologies
Integrating voice AI with legacy systems lets insurers add modern language and speech capabilities without rebuilding their core platforms, which is the essence of legacy system extension.
You keep the backbone, but upgrade what the caller actually experiences.
In practice, this looks like:
Intent understanding and dialog control with IBM Watson Assistant or Google Dialogflow, plus voice command handling via Amazon Lex.
Multilingual speech-to-text and text-to-speech with Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services across voice and digital channels.
Secure legacy data access through AWS API Gateway or Apigee Edge using OAuth 2.0 and JWT, with centralized logging for audit trails.
Faster launches of voice-driven services like quotes, micro-insurance, and real-time claim updates using OpenLegacy, Nividous RPA, MuleSoft Anypoint, Dell Boomi, AWS Lambda, or Azure Functions.
These tools don’t replace your core systems. They wrap them with a modern voice layer that’s easier to scale, secure, and improve over time.
Insurance-ready voice AI in practice
One standout solution is Strada.
It delivers instant AI-powered phone agents designed specifically for insurance tasks like renewals, First Notice of Loss claims, policy servicing, and quote intake. Strada handles repetitive calls and smartly routes complex issues to humans.
This cuts costs, boosts efficiency, and elevates customer satisfaction. Best of all, Strada’s AI is trained on insurance lingo, ensuring its voice understanding is spot-on. It integrates smoothly via APIs or your current AMS/CRM – no expensive redevelopment needed.
Before you move forward, it’s important to understand the challenges teams usually face.
What challenges come with integrating legacy insurance systems for voice AI?
Integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems isn’t always smooth sailing. You’ll face several hurdles, but knowing them upfront helps you tackle each one effectively.
Security and integration complexity
Integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems often surfaces issues that were hidden for years. Most of them aren’t blockers, but they do add friction if you don’t plan for them early.
In practice, teams usually run into the following challenges:
Legacy systems lacking encryption and relying on outdated protocols like SNA or CIFS.
Missing or outdated APIs that require reverse-engineering batch logic or data access layers.
Strict compliance requirements across claims, underwriting, and policy workflows under HIPAA or GDPR.
High technical debt combined with limited internal expertise and incomplete documentation.
Addressing them upfront with proper security layers, clear integration boundaries, and realistic expectations makes voice AI rollouts far more predictable.
Operational constraints and scalability limits
Testing is another challenge. Voice AI needs clean, timely data, but legacy systems often work in batches, not in real time. Balancing this mismatch means setting up detailed integration tests using voice simulation tools like Postman or Botium.
And don’t forget scalability. Legacy infrastructure wasn’t designed for low-latency, real-time interactions. Adding caching layers or event-driven messaging with Apache Kafka or IBM MQ can help meet voice AI’s speed demands.
Supporting employees through AI adoption
Finally, your workforce will need support. They’ll juggle new voice AI tools alongside old processes. Retraining and managing change smoothly, with frameworks like ADKAR or Kotter, makes adoption easier.
You might be wondering how to overcome these challenges seamlessly. Strada offers no-engineering-lift AI agents that plug right into your existing telephony and insurance systems.
Its workflow automation cuts down manual handoffs, speeds ROI, and keeps security and compliance on point.
Plus, Strada’s forward-deployed team guides you through security, performance, and integration best practices, easing your legacy exposure worries and boosting your voice AI success.
The good news is that these challenges are well understood. There are proven integration approaches that work reliably in insurance.
How can you integrate legacy systems with voice AI? Practical approaches and tools
Integrating legacy systems with voice AI might sound tricky, but with the right approaches, you can make it work smoothly. You’ll learn practical ways to connect your older insurance systems with new voice AI tech without massive overhauls.
Let’s break down the key methods and tools that enable legacy system extension in practice.
Core integration patterns for legacy systems
There are a few proven ways teams connect voice AI to legacy systems. Seeing them visually makes the trade-offs clearer.

First up, API strategies are your best friend. By exposing or wrapping legacy features into RESTful, SOAP, or GraphQL APIs, you create a clear bridge for voice AI to interact with your systems.
Use API design tools like Swagger/OpenAPI or RAML to document these interfaces, so everyone understands how they work.
During development, Postman helps you test and tweak APIs easily. This approach enables you to extend legacy systems without rewriting them.
If APIs feel insufficient or too complex, middleware and Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) platforms come to the rescue. Tools like MuleSoft Anypoint, WSO2, or IBM Integration Bus orchestrate communication between your voice AI platform and both legacy and modern systems.
They handle protocol translation and message enrichment, which means your voice AI speaks the right language behind the scenes.
Another handy option is Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) – cloud tools like Dell Boomi, Microsoft Power Automate, and Zapier simplify connecting different systems quickly.
They offer drag-and-drop interfaces, which get your integrations off the ground fast and with minimal coding. If you want to automate routine workflows without deep technical involvement, this is ideal.
Sometimes, your legacy system might not have APIs or be too complex to open up directly. That’s where Robotic Process Automation (RPA) steps in. Bots built with platforms like Nividous RPA or UIPath can mimic human interactions with legacy screen interfaces.
This way, you automate data entry or retrieval tasks while keeping your existing systems intact.
At this point, it helps to pause and look at these integration options side by side. Each one solves a different problem, and seeing them together makes the trade-offs easier to understand.
Integration approach | What it’s best for | When teams use it | Main trade-off |
APIs (REST, SOAP, GraphQL) | Direct system access | You control the backend | Requires dev effort |
Middleware / ESB | Connecting many systems | Large, complex stacks | Higher setup complexity |
iPaaS | Fast cloud integrations | Speed matters most | Less customization |
RPA | No APIs available | UI-only legacy systems | Fragile at scale |
As systems evolve, integration often becomes a mix of methods – bridging on-premise legacy platforms with cloud services while modernizing components step by step.
Many organizations find combining cloud and on-premises tech beneficial. Using solutions such as OpenLegacy Hub, you can create a hybrid integration environment.
This setup allows secure and scalable API exposure from legacy systems connected smoothly to cloud-based voice AI services.
If you plan to evolve your tech stack more gradually, consider breaking down your old monolith systems into microservices using frameworks like Spring Boot or Quarkus.
Smaller, modular components make it easier to attach voice AI features incrementally, while improving scalability.
Scalability, reliability, and operational readiness
To make communication more resilient and scalable, introduce event-driven messaging. Platforms like Apache Kafka, IBM MQ, or RabbitMQ support asynchronous message queues.
This reduces synchronization bottlenecks and helps your voice AI handle real-time data flows without overloading legacy systems.
When modernizing hosting environments, containerization with Docker and Kubernetes lets you run legacy apps in portable, cloud-friendly setups. This approach also paves the way for DevOps practices like continuous deployment, speeding up feature rollout.
Of course, you’ll want to keep everything secure. Implement industry-standard security frameworks such as OAuth 2.0, JWT, multi-factor authentication, and TLS encryption for data at rest and in transit. API gateways like Apigee, AWS API Gateway, or IBM API.
Connect centrally manage security policies, making your integrations safer and compliant with insurance regulations.
To keep your integrations stable and efficient, focus on API management and monitoring. Use tools like Kong or Tyk for API gateway functions.
Meanwhile, monitoring stacks like ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Prometheus, and Grafana give you clear visibility and help catch issues before they snowball.
If you want to speed up integration projects and empower non-developers, low-code/no-code frameworks such as Microsoft PowerApps, Mendix, and OutSystems enable rapid voice AI deployments.
These platforms open the door for citizen developers to build and adjust integrations without waiting for IT cycles.
For building your voice AI layer, go with popular platforms like Google Dialogflow or Amazon Lex for voice interfaces and intent recognition. IBM Watson Assistant offers sophisticated dialog management, while Microsoft Azure Bot Service supports multi-modal interactions, combining voice, text, and more.
One last game changer: establish robust CI/CD pipelines. Tools like Azure DevOps, Jenkins, or GitLab CI let you integrate API development and voice AI deployment seamlessly.
By this point, it helps to see how all production pieces come together as one system.
Component | What it enables | Why it matters |
Event-driven messaging | Async processing | Handles traffic spikes |
Containers | Portable runtimes | Safer scaling |
Security frameworks | Controlled access | Protects sensitive data |
API management | Traffic control | Prevents overload |
Monitoring | System visibility | Faster incident response |
CI/CD pipelines | Automated releases | Continuous improvement |
Continuous integration ensures you can roll out improvements quickly and reliably, keeping your systems in sync.
A faster path with insurance-ready voice AI
To make things even simpler, consider Strada’s plug-and-play AI phone agents. These agents integrate natively with legacy AMS, CRM, and telephony platforms, cutting down engineering effort drastically and speeding up deployment.
Plus, Strada Workflows empower you with drag-and-drop, no-code automation for post-call actions, like triggering follow-ups, updating your CRM, or starting multi-channel communications – connecting your voice AI directly to business processes without writing custom code.

In summary, integrating legacy systems with voice AI isn’t magic – it’s all about choosing the right combination of APIs, middleware, automation tools, and platforms.
By mixing and matching these practical solutions, you’ll extend your legacy systems’ value and make voice AI work seamlessly for your insurance business.
Once the approach is clear, execution becomes manageable. Breaking integration into clear steps reduces risk and keeps teams aligned.
How to plan and execute integration step-by-step
When you’re integrating voice AI with legacy insurance systems, a solid plan is your best friend.
You’ll want to move carefully but confidently, especially when avoiding full legacy system replacement.
Here’s how to break it down:
Assess legacy system landscape
Start by taking stock of what you have. Make a detailed list of legacy applications, data stores, batch jobs, and middleware components.
Gather architecture documents, check existing APIs, and see how complete the documentation is using tools like Enterprise Architect or Sparx Systems.
Also, look at how often these systems are used and which ones are critical. This gives you the big picture and helps avoid surprises later.
Define voice AI use cases aligned to business priorities
Next, pick voice AI use cases that matter most to your business. Think automation for claims intake via voice bots, virtual assistants answering policy queries, or voice-driven billing updates.
Get input from stakeholders to make sure these ideas deliver real value and a solid return on investment.
Select integration technologies
Choose the right tools based on what your legacy systems can handle and what your voice AI requires. You might use middleware, API platforms, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), or a combination.
Vendors like OpenLegacy, Nividous, MuleSoft, or Dell Boomi are strong contenders. Look for solutions that scale well, keep data secure, and come with good support.
To keep things practical, here’s a quick checklist for this step:
Confirm legacy system’s API readiness.
Decide between middleware, RPA, or hybrid approach.
Evaluate vendor scalability and security features.
Ensure support and training availability.
Once these basics are clear, teams can move forward with confidence and avoid costly rework later.
Build prototypes and conduct integration testing
Create prototypes in sandbox or staging environments. Use API testing tools like Postman or SoapUI to validate connections. For your voice AI, employ testing suites such as Botium to check intent accuracy and user experience.
Load testing is key too, to avoid performance issues. Also, double-check compliance with data security and privacy rules here.
For example, while testing, you can incorporate pilot AI phone agents powered by Strada, which come with built-in insurance workflows like claim filing and policy servicing. This helps validate benefits early, with minimal impact on your live legacy systems.
Strada’s pre-built insurance use cases and domain models speed up your proof of concept and make deployment smoother.
Optimize integrations
Once testing is done, tune the system for speed and accuracy. Improve API response times and boost voice AI’s intent recognition. Don’t forget security hardening – set up strong authentication and encryption.
Also, put rollback plans and incident response procedures in place to keep things stable and easy to recover.
Document everything and train your teams
Hungry for smooth operations? Document every integration workflow clearly. Create runbooks, detailed API documentation, and user manuals. Then, run training sessions for IT and customer service teams.
Using knowledge bases and learning management systems will help keep everyone up to speed over time.
Plan for scalability and maintainability
Voice AI integration shouldn’t be treated as a one-off project. Planning for growth early helps avoid brittle setups that break as usage, traffic, or requirements change.
In practice, this means:
Designing integrations so components can scale independently as call volumes grow.
Using containerization and cloud-ready patterns to simplify deployment and rollback.
Putting version control and change management in place to prevent breaking updates.
Accounting for future voice AI features to avoid reworking integrations later.
This approach keeps integrations stable over time and allows teams to evolve voice AI capabilities without constantly revisiting core system architecture.
Set up monitoring and continuous improvement
Finally, build monitoring dashboards using tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or the ELK stack. These help you track voice AI and API health in real time. Set alerts for any SLA breaches or odd behavior.
Establish feedback loops with business users and tech teams to keep refining performance continuously.
Supporting your integration work, integrate DevOps tools like Azure DevOps or AWS CodePipeline to automate builds and deployments. The Nividous Control Center is another great tool to keep RPA bots healthy and governed properly.
By following these steps, you turn the daunting task of legacy system modernisation and voice AI integration into a manageable, successful journey. You’ll not only make your systems smarter but also prepare your insurance operations for the future.
So what does all this effort enable in practice? Let’s look at how insurers actually use voice AI today!
What are common voice AI use cases integrated with legacy systems in insurance?
You’re probably wondering how voice AI can actually work with those old legacy systems insurers use. The good news? Voice AI integration is already transforming core insurance operations, making life easier for customers, agents, and insurers alike.
Let’s walk through a simple, real-world example to see how this works in practice.

And, let’s walk through some of the most practical and common use cases where voice AI teams up with legacy systems.
Core insurance operations powered by voice AI
First off, customer service is a big one. Conversational AI can answer policy questions, explain coverage details, give claim status updates, and handle FAQs. This reduces the load on call centers by letting voice assistants tap directly into those backend legacy databases for real-time info.
That means customers get instant answers without waiting on hold, and agents can focus on more complex tasks.
Another popular use is claims filing and status tracking. You can use voice commands to start a new claim, leave voice notes about incidents, or check the progress of existing claims.
The AI talks to the legacy claims processing systems behind the scenes, making this process faster and less manual.
Extended and emerging insurance use cases
Here’s a quick list to show you how voice AI helps with other key insurance tasks by integrating with legacy systems:
Underwriting assistance → Capture data from customers or agents by voice, then quickly query and update legacy underwriting engines through APIs to adjust policies on the fly.
Fraud detection → Voice-guided workflows offer real-time risk alerts, helping investigators adjust their approach using AI models connected to older risk databases.
Automated payment reconciliation → Confirm payments or trigger reconciliation checks via simple voice commands, with secure links to legacy financial platforms like Oracle EBS.
Micro-insurance access → In emerging markets, mobile voice platforms enable instant policy purchases or inquiries, all backed by middleware that bridges with legacy policy admin systems.
You’ll find several top voice AI platforms supporting these integrations. Google Dialogflow shines for intent mapping and multi-channel voice experiences, while IBM Watson Assistant lets you build customizable virtual agents that feel natural on calls.
Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services nails the speech-to-text and text-to-speech tasks, and Amazon Lex powers Alexa-enabled skills tailored for insurance workflows.
Voice AI use cases in production
In practical terms, Strada is a great example of making this work on the ground. Their AI phone agents handle thousands of calls, from quote intake and First Notice of Loss (FNOL) reporting to renewals and agent lead qualification.
These agents trigger workflows that dig deep into legacy systems, AMS, CRM, and others, automating complex tasks without replacing those legacy systems entirely.
Strada also automates certificate issuance requests and claims intake by interfacing directly with legacy policy and claims backends. This results in quick, personalized responses that boost customer satisfaction and make agents more productive.

You can see how this smart integration strikes the perfect balance – leveraging existing systems while adding exciting new voice AI capabilities.
By focusing on integrating voice AI with current legacy systems instead of replacing them wholesale, insurers gain efficiency and improve customer interactions rapidly.
You’ll learn that this approach not only cuts costs but also creates seamless, hands-free experiences customers expect.
At this point, the pattern is clear. Integration allows insurers to move forward without disrupting systems they already rely on.
Why integration beats replacement and how voice AI unlocks legacy value
You’ll find that integrating voice AI with your legacy systems makes more sense than pursuing a broad legacy system replacement strategy. It protects your big investments, avoids the high costs and risks of rewrites, and lets you innovate faster by layering AI over systems you already trust.
Voice AI boosts customer experience and operational agility by enabling real-time, natural conversations powered by your existing data.
To get started, try these practical steps:
Launch a pilot or proof-of-concept with platforms like OpenLegacy, Nividous, or MuleSoft to see real business impact quickly.
Engage expert partners early, align clearly with your business goals, and invest in ongoing training and monitoring for long-term success.
For insurance specifically, consider Strada. It’s a ready-to-use AI phone agent platform designed for deep legacy integration, zero engineering lift, and quick wins in call automation and AI workflows.
This way, you get immediate boosts in operations and revenue without the headaches of full legacy system modernisation or replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can voice AI work with very old insurance systems?
Yes. Voice AI can connect through APIs, middleware, or RPA, allowing interaction with even COBOL-based mainframes without replacing existing core insurance platforms.
How long does legacy system integration with voice AI usually take?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Do insurers need to replace their core systems to use voice AI?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Can voice AI scale during peak call volumes?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
How does voice AI reduce call center workload?
Framer is a design tool that allows you to design websites on a freeform canvas, and then publish them as websites with a single click.
Table of Contents
Carriers, MGAs, and brokers scale revenue-driving phone calls with Strada's conversational AI platform.
Start scaling with voice AI agents today
Join innovative carriers and MGAs transforming their calls with Strada.
© 2026 Strada API, Inc.
© 2026 Strada API, Inc.
© 2026 Strada API, Inc.
